日志配置及常用 CRUD
作者:村雨遥
不要哀求,学会争取,若是如此,终有所获
🎈 号外
最近,公众号之外,建立了微信交流群,不定期会在群里分享各种资源(影视、IT 编程、考试提升……)&知识。如果有需要,可以扫码或者后台添加小编微信备注入群。进群后优先看群公告,呼叫群中【资源分享小助手】,还能免费帮找资源哦~
前言
上一篇文章中我们讲了 Mybatis-Plus 的定义以及相关特点,并从零开始编写了一个 SpringBoot + Mybatis-Plus 的实例。今天我们就来看看,如何利用 MP 来实现对数据库的增删改查。
日志配置
使用 MP 时,默认是不打印任何 SQL 语句的。而为了方便日常开发工作的调试,我们需要联合控制台和各种数据可视化工具进行语句的拼接检查,因此我们利用 MP 自带的日志功能,在控制台输出我们的 SQL 语句,从而方便我们调试。
在配置文件 application.yml (IDEA 默认生成的配置文件为 application.properties)中,加入一下配置,这样 MP 就会在控制台中打印完整带参数的 SQL 语句,方便我们查看。
mybatis-plus:
configuration:
log-impl: org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImplMapper CRUD 使用方法
首先我们来看 Mapper 层 CRUD 涉及的一些方法,Mapper 层主要继承自 BaseMapper 接口,里边实现了各种用于操作数据库的增删改查的方法,以下我们就来看看日常我们常用的一些方法。
package com.cunyu.employee.mapper;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.mapper.BaseMapper;
import com.cunyu.employee.entity.Employee;
/**
* Created with IntelliJ IDEA.
*
* @author : cunyu
* @version : 1.0
* @project : Employee
* @package : com.cunyu.employee.mapper
* @className : EmployeeMapper
* @createTime : 2021/8/7 17:45
* @description : 员工 Mapper 类
*/
public interface EmployeeMapper extends BaseMapper<Employee> {
}insert 操作
首先是插入数据,insert 方法中,传入我们所要插入数据库的实体对象作为参数即可。
- 方法声明
/**
* 插入一条记录
*
* @param entity 实体对象
*/
int insert(T entity);- 插入实例
package com.cunyu.employee;
import com.cunyu.employee.entity.Employee;
import com.cunyu.employee.mapper.EmployeeMapper;
import org.junit.Assert;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
class EmployeeApplicationTests {
@Test
void contextLoads() {
}
@Autowired
private EmployeeMapper employeeMapper;
@Test
void testInsert() {
Employee employee = new Employee();
employee.setId(4L);
employee.setName("赵六");
employee.setSex("男");
employee.setEmail("zhaoliu@cunyu1943.com");
Assert.assertEquals(1, employeeMapper.insert(employee));
System.out.println("插入成功");
}
}- 测试结果
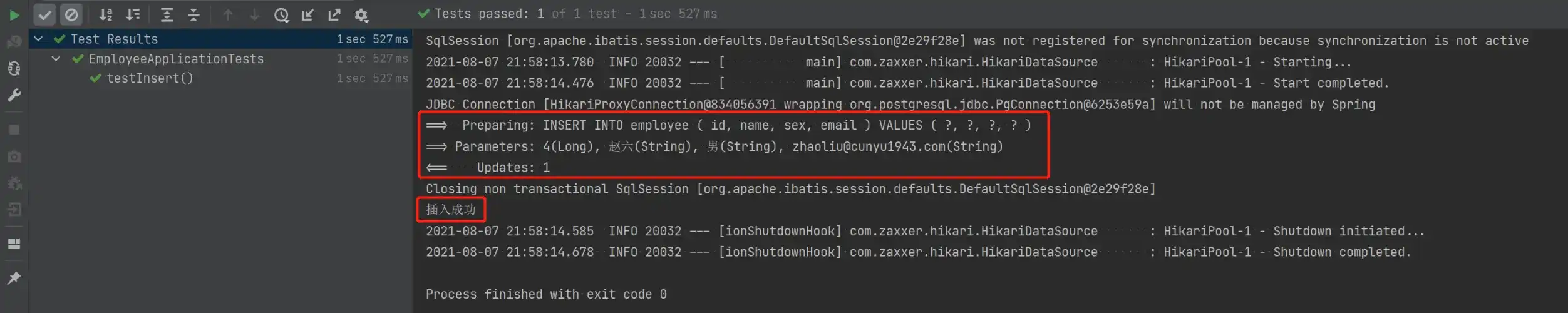
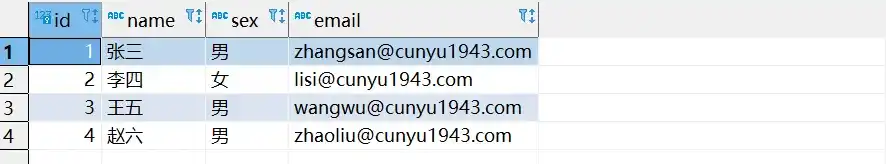
- 数据插入后的数据库
select 操作
相比于插入数据操作,查询数据的方法就要更多,而且还能实现批量查询和条件查询。
- 根据主键查询
将所要查询数据的主键作为参数传入我们的 selectById 方法中,即可实现。
- 方法声明
/**
* 根据 ID 查询
*
* @param id 主键ID
*/
T selectById(Serializable id);- 查询实例
package com.cunyu.employee;
import com.cunyu.employee.entity.Employee;
import com.cunyu.employee.mapper.EmployeeMapper;
import org.junit.Assert;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
class EmployeeApplicationTests {
@Test
void contextLoads() {
}
@Autowired
private EmployeeMapper employeeMapper;
@Test
void testSelectById() {
Employee employee = employeeMapper.selectById(3);
System.out.println(employee);
}
}- 测试结果
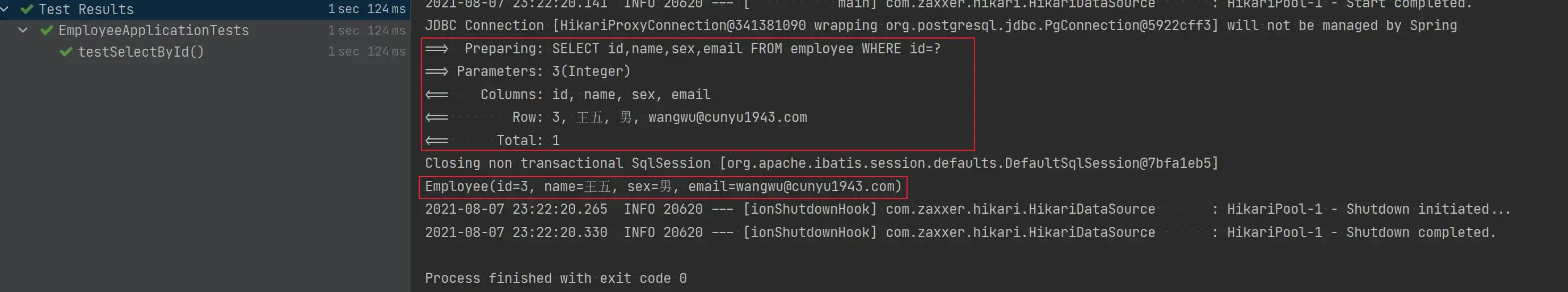
- 根据主键批量查询
上一个方法每次只能查询一条记录,如果我们想要查询多条数据记录,那么就可以将要查询数据的主键列表传入 selectBatchIds 方法即可。
- 方法声明
/**
* 查询(根据ID 批量查询)
*
* @param idList 主键ID列表(不能为 null 以及 empty)
*/
List<T> selectBatchIds(@Param(Constants.COLLECTION) Collection<? extends Serializable> idList);- 批量查询实例
package com.cunyu.employee;
import com.cunyu.employee.entity.Employee;
import com.cunyu.employee.mapper.EmployeeMapper;
import org.junit.Assert;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
class EmployeeApplicationTests {
@Test
void contextLoads() {
}
@Autowired
private EmployeeMapper employeeMapper;
@Test
void testSelectBatchIds() {
List<Integer> ids = new ArrayList<>();
ids.add(1);
ids.add(4);
List<Employee> employeeList = employeeMapper.selectBatchIds(ids);
System.out.println(employeeList);
}
}- 测试结果
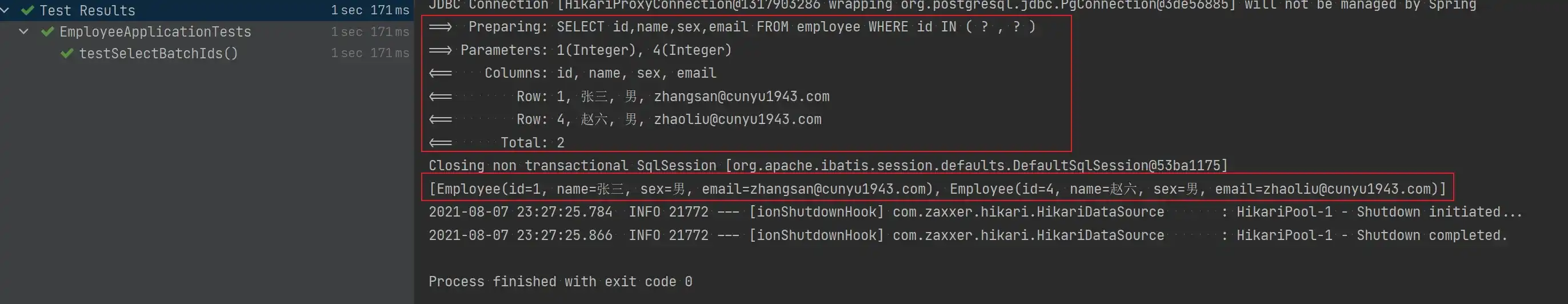
- 根据多条件查询
除开支持主键查询外,MP 还支持条件查询,只要将我们的条件传入 Map 列表中,然后将其作为 selectByMap 方法的参数即可,其中传入 Map 的 key 对应我们数据库中的字段,而 value 则对应字段的值。
- 方法声明
/**
* 查询(根据 columnMap 条件)
*
* @param columnMap 表字段 map 对象
*/
List<T> selectByMap(@Param(Constants.COLUMN_MAP) Map<String, Object> columnMap);- 条件查询实例
package com.cunyu.employee;
import com.cunyu.employee.entity.Employee;
import com.cunyu.employee.mapper.EmployeeMapper;
import org.junit.Assert;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
class EmployeeApplicationTests {
@Test
void contextLoads() {
}
@Autowired
private EmployeeMapper employeeMapper;
@Test
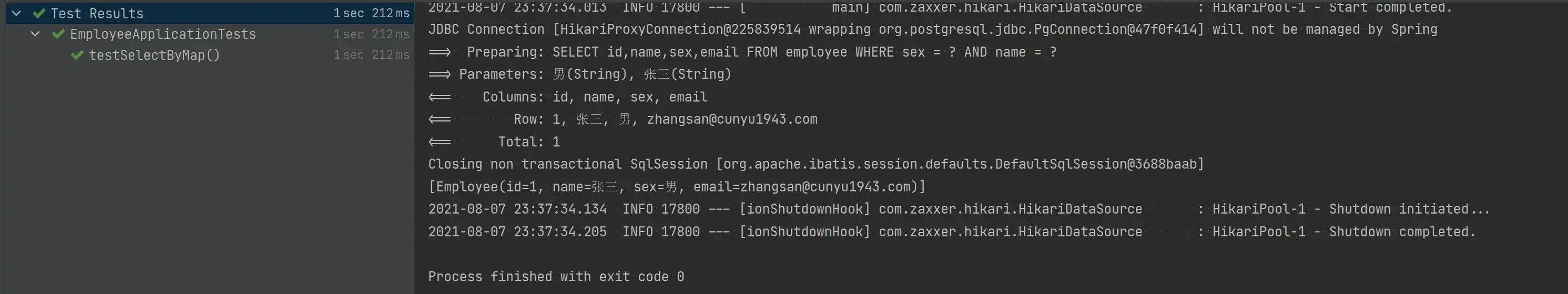
void testSelectByMap() {
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("sex", "男");
map.put("name", "张三");
System.out.println(employeeMapper.selectByMap(map));
}
}- 测试结果
update 操作
更新操作,主要是根据我们数据库的主键进行查询,将对应主键的实体对象传入 updateById 方法即可。
- 方法声明
/**
* 根据 ID 修改
*
* @param entity 实体对象
*/
int updateById(@Param(Constants.ENTITY) T entity);- 更新实例
package com.cunyu.employee;
import com.cunyu.employee.entity.Employee;
import com.cunyu.employee.mapper.EmployeeMapper;
import org.junit.Assert;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
class EmployeeApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private EmployeeMapper employeeMapper;
@Test
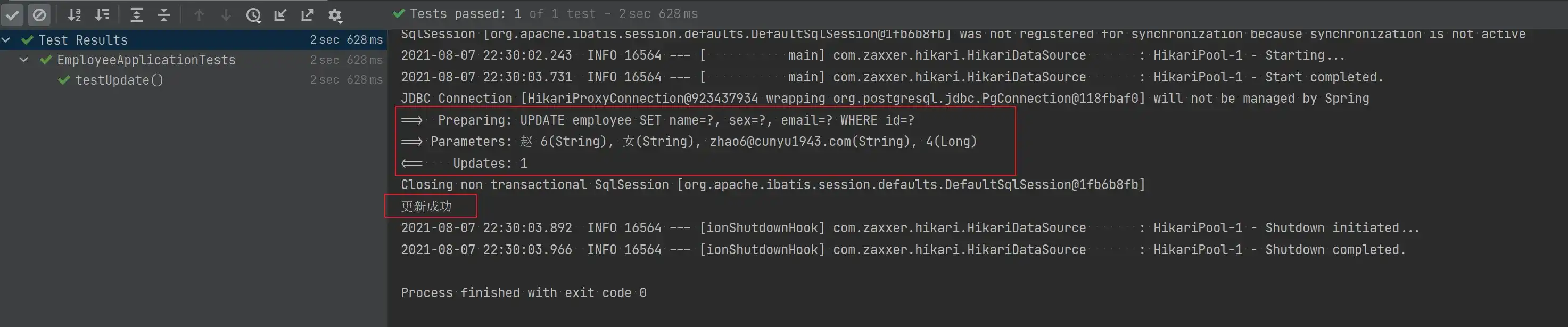
void testUpdate() {
Employee employee = new Employee();
employee.setEmail("zhao6@cunyu1943.com");
employee.setName("赵 6");
employee.setSex("女");
employee.setId(4L);
Assert.assertEquals(1, employeeMapper.updateById(employee));
System.out.println("更新成功");
}
}- 测试结果
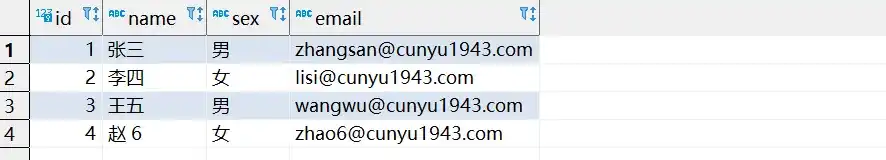
- 数据更新后的数据库
delete 操作
删除操作,既可以根据主键删除一条记录,也能根据主键列表实现批量删除,还能根据条件来进行删除。
- 根据主键删除一条数据
将所要删除记录的主键作为参数传入 deleteById 方法即可。
- 方法声明
/**
* 根据 ID 删除
*
* @param id 主键ID
*/
int deleteById(Serializable id);- 删除实例
package com.cunyu.employee;
import com.cunyu.employee.entity.Employee;
import com.cunyu.employee.mapper.EmployeeMapper;
import org.junit.Assert;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
class EmployeeApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private EmployeeMapper employeeMapper;
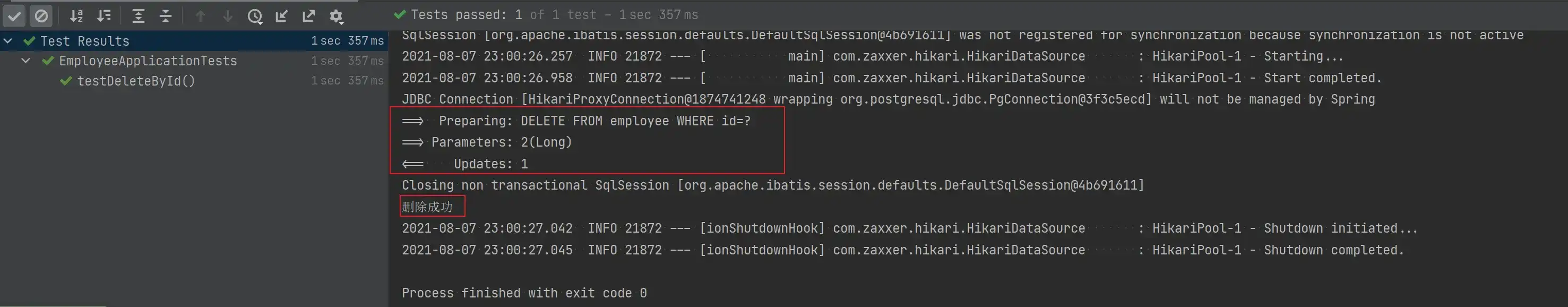
@Test
void testDeleteById() {
Assert.assertEquals(1, employeeMapper.deleteById(2L));
System.out.println("删除成功");
}
}- 测试结果
- 删除数据后的数据库
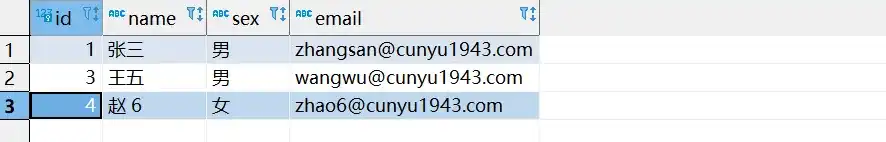
- 根据条件删除
根据条件删除同样是讲条件传入 Map 中,然后将 Map 作为参数传入 deleteByMap 方法,其中 key 对应数据库中的字段,value 对应字段的值。
- 方法声明
/**
* 根据 columnMap 条件,删除记录
*
* @param columnMap 表字段 map 对象
*/
int deleteByMap(@Param(Constants.COLUMN_MAP) Map<String, Object> columnMap);- 删除实例
package com.cunyu.employee;
import com.cunyu.employee.entity.Employee;
import com.cunyu.employee.mapper.EmployeeMapper;
import org.junit.Assert;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
class EmployeeApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private EmployeeMapper employeeMapper;
@Test
void testDeleteByMap() {
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("name", "赵 6");
Assert.assertEquals(1, employeeMapper.deleteByMap(map));
System.out.println("删除成功");
}
}- 测试结果
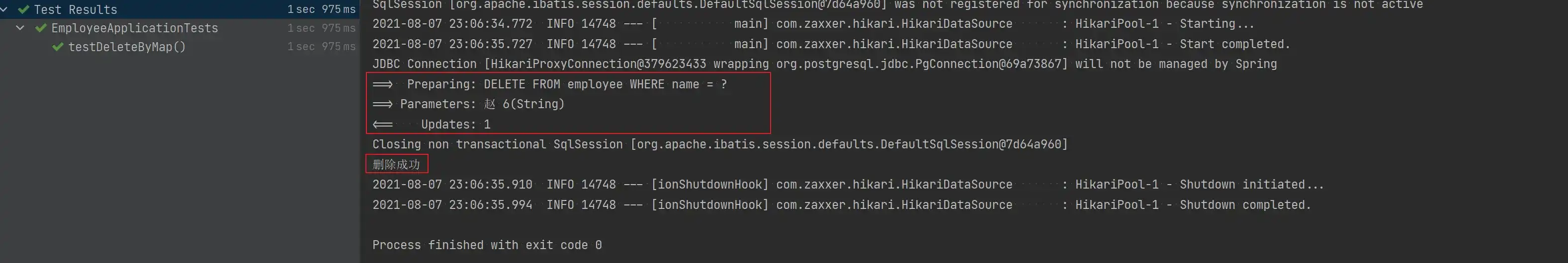
- 删除数据后的数据库
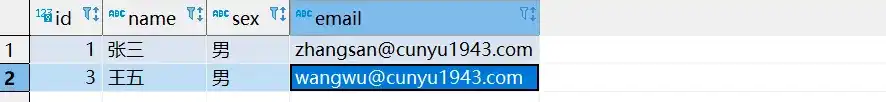
- 根据主键批量删除
将要删除记录的主键传入集合中,然后将集合作为 deleteBatchIds 方法的参数即可。
- 方法声明
/**
* 删除(根据ID 批量删除)
*
* @param idList 主键ID列表(不能为 null 以及 empty)
*/
int deleteBatchIds(@Param(Constants.COLLECTION) Collection<? extends Serializable> idList);- 批量删除实例
package com.cunyu.employee;
import com.cunyu.employee.entity.Employee;
import com.cunyu.employee.mapper.EmployeeMapper;
import org.junit.Assert;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
class EmployeeApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private EmployeeMapper employeeMapper;
@Test
void testDeleteBatchIds() {
List<Integer> ids = new ArrayList<>();
ids.add(1);
ids.add(3);
Assert.assertEquals(2, employeeMapper.deleteBatchIds(ids));
System.out.println("删除成功");
}
}- 测试结果
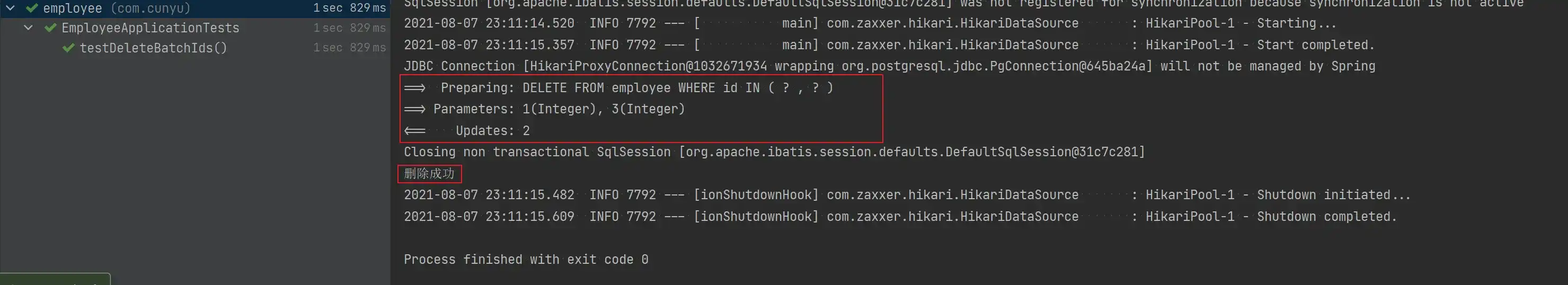
- 删除数据后的数据库
Service CRUD 接口
Service 层继承自 IService 接口,其中的方法和 Mapper 层中所提供的方法功能是一致的,除了方法名有所不同外,其他基本类似,但 Service 层中提供了更为丰富的方法,两者的继承结构如下图所示。
package com.cunyu.employee.service;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.IService;
import com.cunyu.employee.entity.Employee;
/**
* Created with IntelliJ IDEA.
*
* @author : cunyu
* @version : 1.0
* @project : Employee
* @package : com.cunyu.employee.service
* @className : EmployeeService
* @createTime : 2021/8/8 7:52
* @description : 员工服务接口
*/
@Service
public interface EmployeeService extends IService<Employee> {
}package com.cunyu.employee.service.Impl;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.impl.ServiceImpl;
import com.cunyu.employee.entity.Employee;
import com.cunyu.employee.mapper.EmployeeMapper;
import com.cunyu.employee.service.EmployeeService;
/**
* Created with IntelliJ IDEA.
*
* @author : cunyu
* @version : 1.0
* @project : Employee
* @package : com.cunyu.employee.service.Impl
* @className : EmployeeServiceImpl
* @createTime : 2021/8/8 7:53
* @description : 员工服务类实现
*/
@Service
public class EmployeeServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<EmployeeMapper, Employee> implements EmployeeService {
}Save
- 插入一条记录
功能同 Mapper 层中的 insert 方法,只不过方法名不同。
- 方法声明
// 插入一条记录(选择字段,策略插入)
boolean save(T entity);- 插入实例
package com.cunyu.employee;
import com.cunyu.employee.entity.Employee;
import com.cunyu.employee.mapper.EmployeeMapper;
import com.cunyu.employee.service.EmployeeService;
import org.junit.Assert;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
class EmployeeApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private EmployeeService employeeService;
@Test
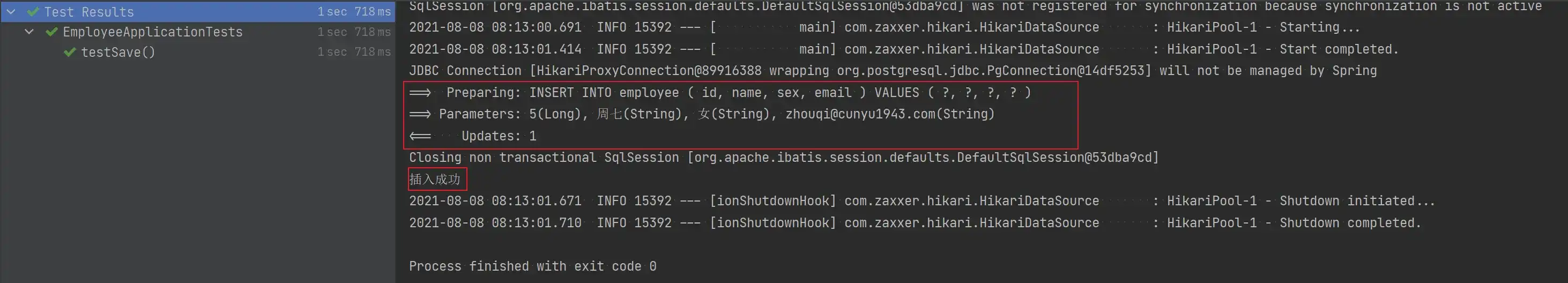
void testSave() {
Employee employee = new Employee();
employee.setId(5L);
employee.setName("周七");
employee.setEmail("zhouqi@cunyu1943.com");
employee.setSex("女");
Assert.assertTrue(employeeService.save(employee));
System.out.println("插入成功");
}
}- 测试结果
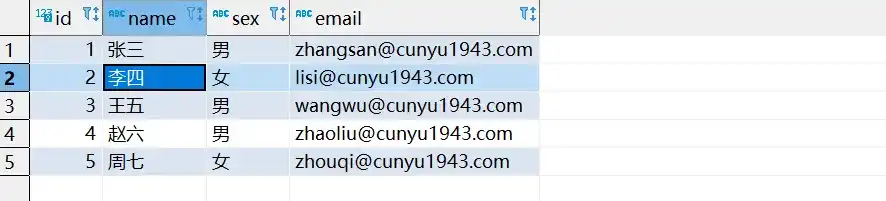
- 插入数据后的数据库
- 批量插入
这里就和 Mapper 层中所有区别,Mapper 层中只支持单次插入,而 Service 层中支持批量插入,而传入的参数就是我们所要传入实体的集合,而且还可以分批次插入和统一插入。
2.1 统一插入
- 方法声明
// 插入(批量)
boolean saveBatch(Collection<T> entityList);- 插入实例
package com.cunyu.employee;
import com.cunyu.employee.entity.Employee;
import com.cunyu.employee.mapper.EmployeeMapper;
import com.cunyu.employee.service.EmployeeService;
import org.junit.Assert;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
@SpringBootTest
class EmployeeApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private EmployeeService employeeService;
@Test
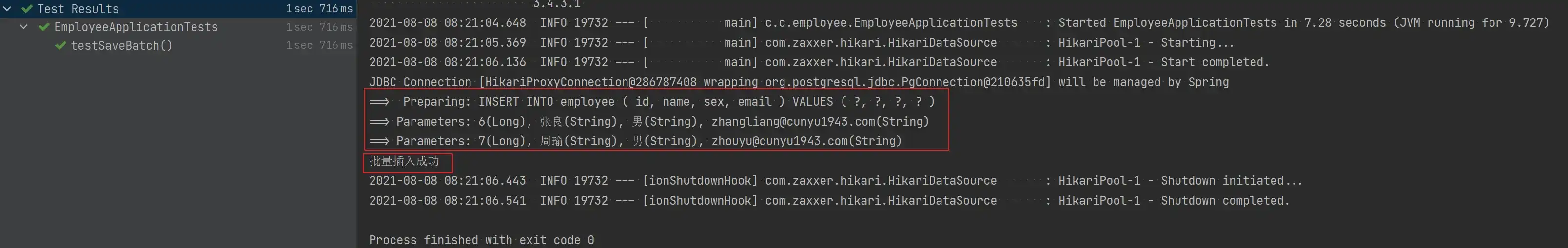
void testSaveBatch() {
Employee employee1 = new Employee();
employee1.setId(6L);
employee1.setEmail("zhangliang@cunyu1943.com");
employee1.setSex("男");
employee1.setName("张良");
Employee employee2 = new Employee();
employee2.setId(7L);
employee2.setEmail("zhouyu@cunyu1943.com");
employee2.setName("周瑜");
employee2.setSex("男");
List<Employee> employeeList = new ArrayList<>();
employeeList.add(employee1);
employeeList.add(employee2);
Assert.assertTrue(employeeService.saveBatch(employeeList));
System.out.println("批量插入成功");
}
}- 测试结果
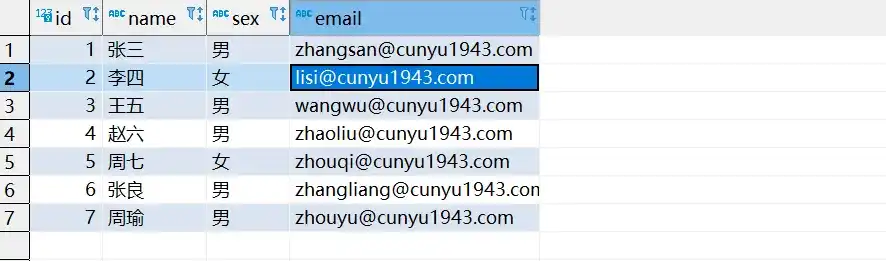
- 统一插入后的数据库
2.2 分批次插入
- 方法声明
// 插入(批量)
boolean saveBatch(Collection<T> entityList, int batchSize);- 分批次插入实例
package com.cunyu.employee;
import com.cunyu.employee.entity.Employee;
import com.cunyu.employee.mapper.EmployeeMapper;
import com.cunyu.employee.service.EmployeeService;
import org.junit.Assert;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
@SpringBootTest
class EmployeeApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private EmployeeService employeeService;
@Test
void testSaveBatch() {
Employee employee1 = new Employee();
employee1.setId(8L);
employee1.setEmail("jialuo@cunyu1943.com");
employee1.setSex("女");
employee1.setName("迦罗");
Employee employee2 = new Employee();
employee2.setId(9L);
employee2.setEmail("zhugeliang@cunyu1943.com");
employee2.setName("诸葛亮");
employee2.setSex("男");
List<Employee> employeeList = new ArrayList<>();
employeeList.add(employee1);
employeeList.add(employee2);
Assert.assertTrue(employeeService.saveBatch(employeeList,2));
System.out.println("批量插入成功");
}
}- 测试结果
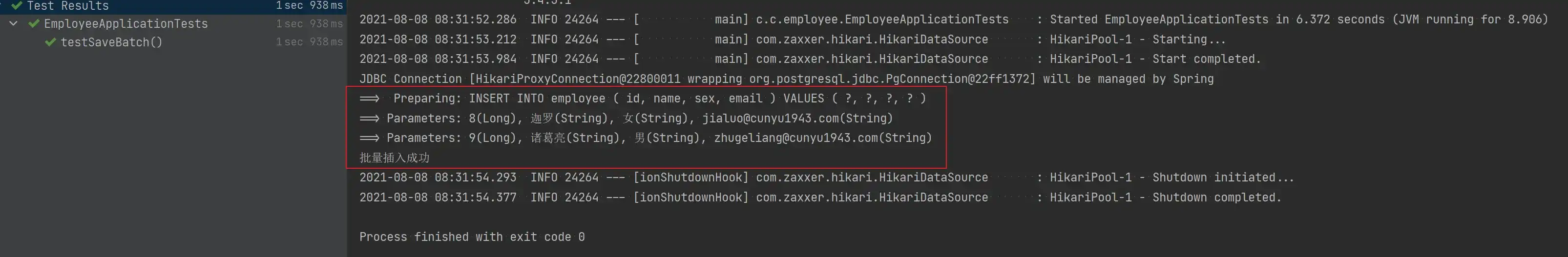
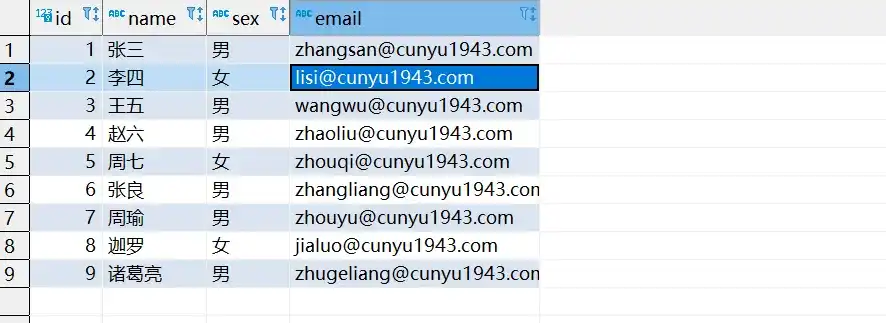
- 分批次插入后的数据库
SaveOrUpdate
- 单条修改插入
- 方法声明
// TableId 注解存在更新记录,否插入一条记录
boolean saveOrUpdate(T entity);- 单条修改插入实例
package com.cunyu.employee;
import com.cunyu.employee.entity.Employee;
import com.cunyu.employee.mapper.EmployeeMapper;
import com.cunyu.employee.service.EmployeeService;
import org.junit.Assert;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
@SpringBootTest
class EmployeeApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private EmployeeService employeeService;
@Test
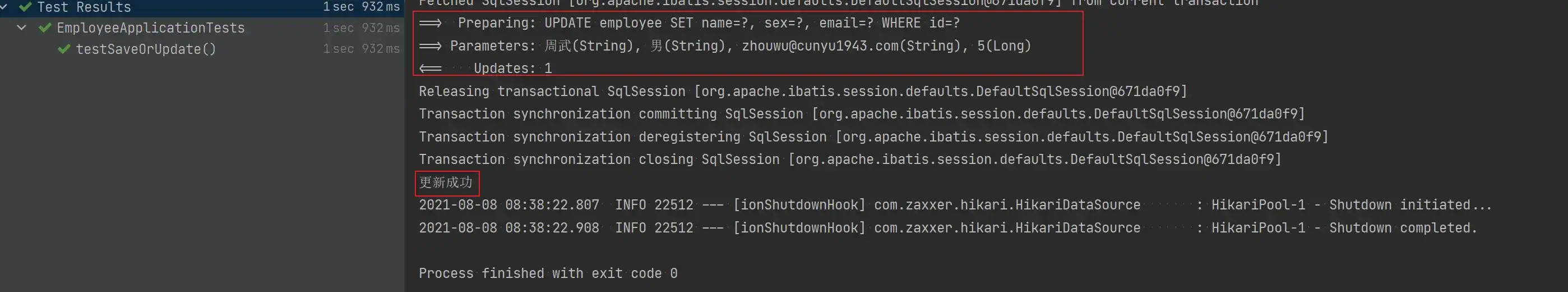
void testSaveOrUpdate() {
Employee employee = new Employee();
employee.setId(5L);
employee.setName("周武");
employee.setEmail("zhouwu@cunyu1943.com");
employee.setSex("男");
Assert.assertTrue(employeeService.saveOrUpdate(employee));
System.out.println("更新成功");
}
}- 测试结果
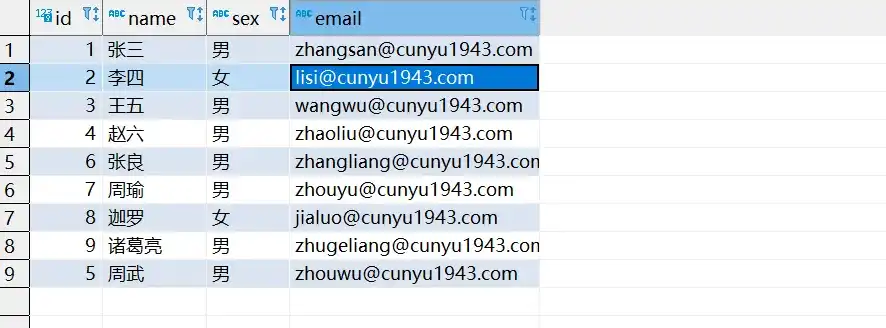
- 修改插入后的数据库
- 批量修改插入
2.1 统一插入
- 方法声明
// 批量修改插入
boolean saveOrUpdateBatch(Collection<T> entityList);- 统一插入实例
package com.cunyu.employee;
import com.cunyu.employee.entity.Employee;
import com.cunyu.employee.mapper.EmployeeMapper;
import com.cunyu.employee.service.EmployeeService;
import org.junit.Assert;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
@SpringBootTest
class EmployeeApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private EmployeeService employeeService;
@Test
void testSaveOrUpdateBatch() {
Employee employee1 = new Employee();
employee1.setId(10L);
employee1.setEmail("zhongwuyan@cunyu1943.com");
employee1.setSex("女");
employee1.setName("钟无艳");
Employee employee2 = new Employee();
employee2.setId(11L);
employee2.setEmail("direnjie@cunyu1943.com");
employee2.setName("狄仁杰");
employee2.setSex("男");
List<Employee> employeeList = new ArrayList<>();
employeeList.add(employee1);
employeeList.add(employee2);
Assert.assertTrue(employeeService.saveOrUpdateBatch(employeeList));
System.out.println("批量修改插入成功");
}
}- 测试结果
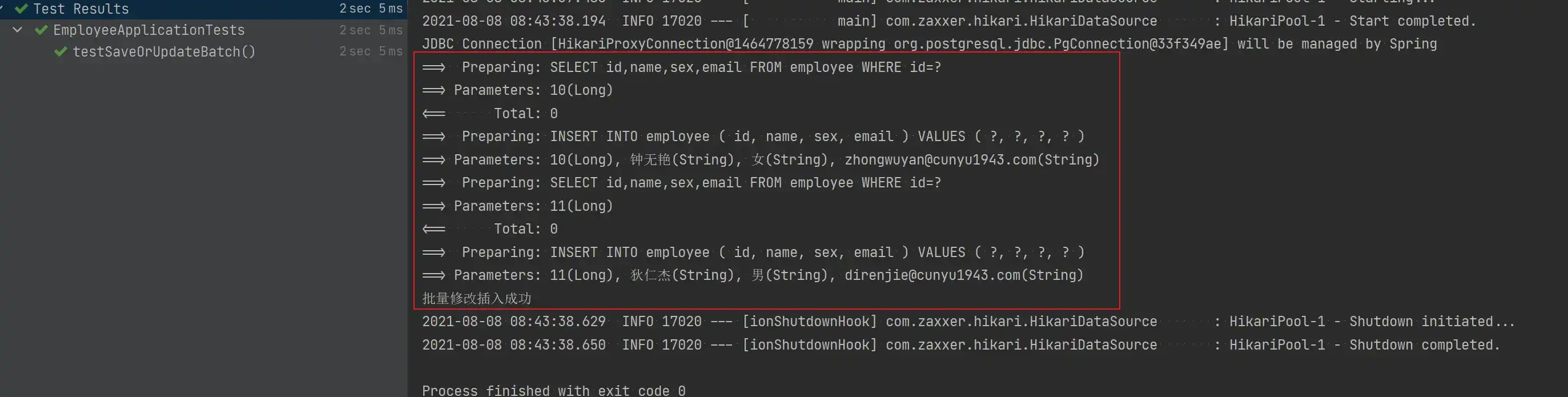
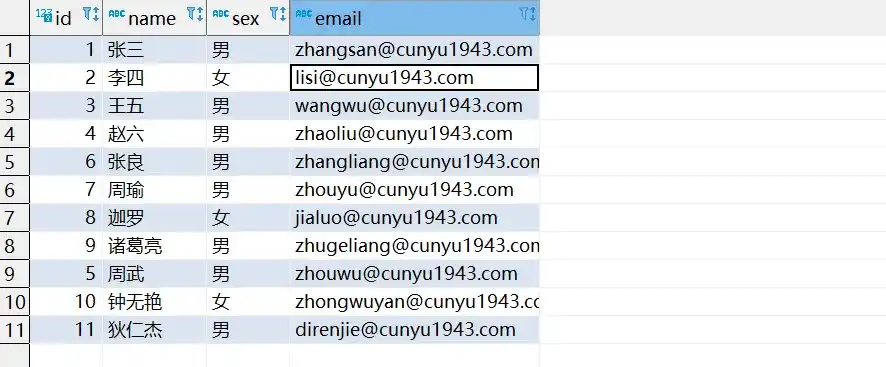
- 统一插入数据后的数据库
2.2 分批次插入
- 方法声明
// 批量修改插入
boolean saveOrUpdateBatch(Collection<T> entityList, int batchSize);- 方法实例
package com.cunyu.employee;
import com.cunyu.employee.entity.Employee;
import com.cunyu.employee.mapper.EmployeeMapper;
import com.cunyu.employee.service.EmployeeService;
import org.junit.Assert;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
@SpringBootTest
class EmployeeApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private EmployeeService employeeService;
@Test
void testSaveOrUpdateBatch() {
Employee employee1 = new Employee();
employee1.setId(12L);
employee1.setEmail("yuji@cunyu1943.com");
employee1.setSex("女");
employee1.setName("虞姬");
Employee employee2 = new Employee();
employee2.setId(13L);
employee2.setEmail("sulie@cunyu1943.com");
employee2.setName("苏烈");
employee2.setSex("男");
List<Employee> employeeList = new ArrayList<>();
employeeList.add(employee1);
employeeList.add(employee2);
Assert.assertTrue(employeeService.saveOrUpdateBatch(employeeList, 2));
System.out.println("批量修改插入成功");
}
}- 测试结果
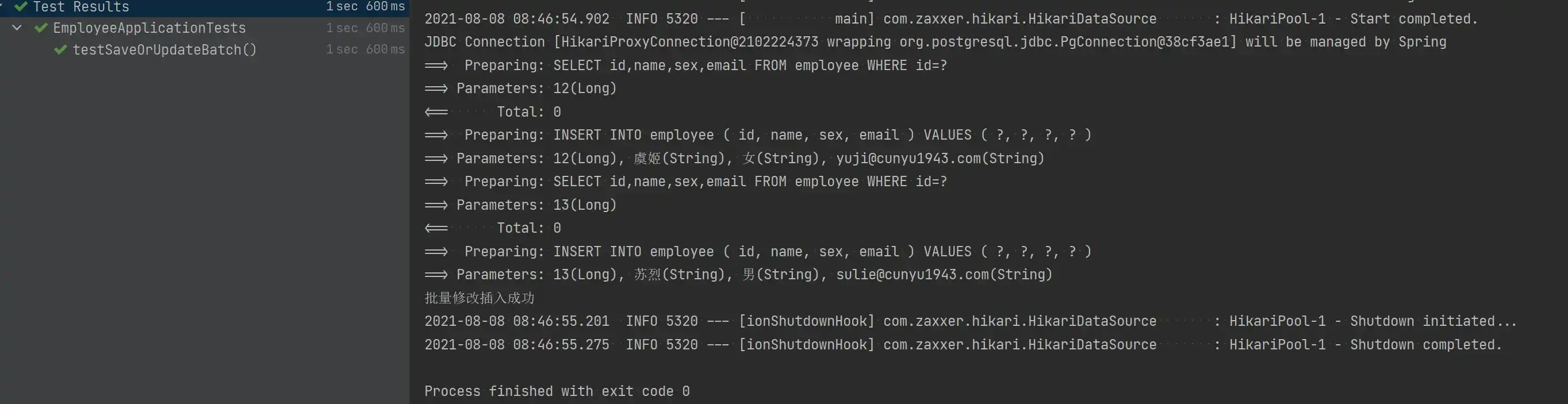
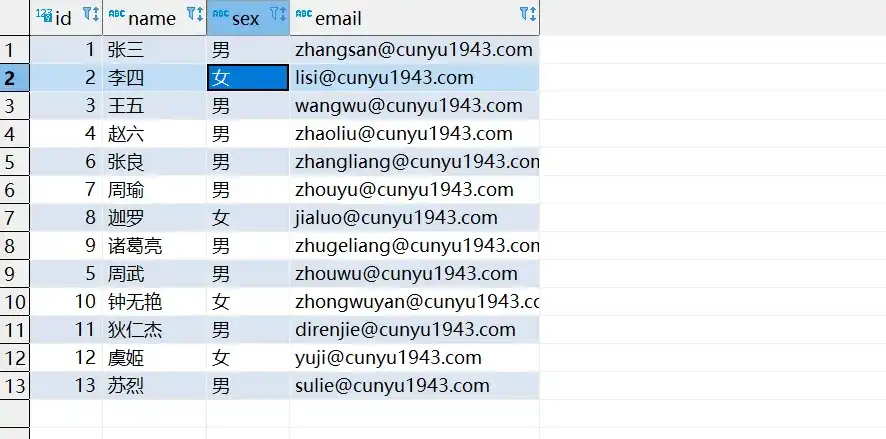
- 分批次插入数据后的数据库
Remove
- 根据 ID 删除
- 方法实例
// 根据 ID 删除
boolean removeById(Serializable id);- 删除实例
package com.cunyu.employee;
import com.cunyu.employee.entity.Employee;
import com.cunyu.employee.mapper.EmployeeMapper;
import com.cunyu.employee.service.EmployeeService;
import org.junit.Assert;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
class EmployeeApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private EmployeeService employeeService;
@Test
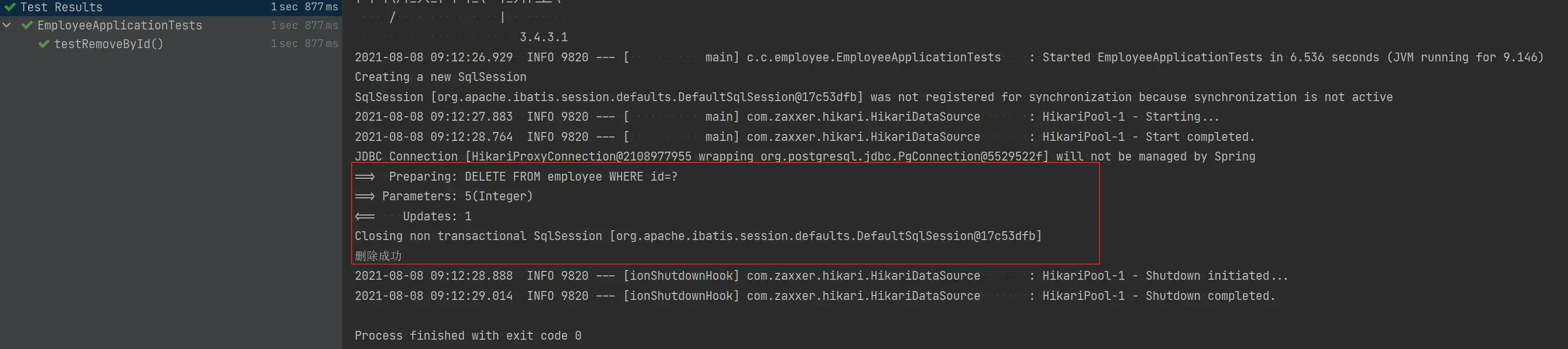
void testRemoveById() {
Assert.assertTrue(employeeService.removeById(5));
System.out.println("删除成功");
}
}- 测试结果
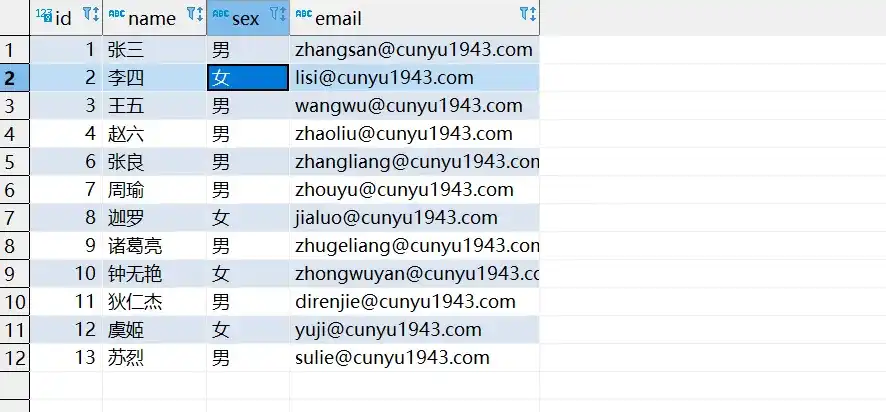
- 根据条件删除
- 方法声明
// 根据 columnMap 条件,删除记录
boolean removeByMap(Map<String, Object> columnMap);- 按条件删除实例
package com.cunyu.employee;
import com.cunyu.employee.entity.Employee;
import com.cunyu.employee.mapper.EmployeeMapper;
import com.cunyu.employee.service.EmployeeService;
import org.junit.Assert;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@SpringBootTest
class EmployeeApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private EmployeeService employeeService;
@Test
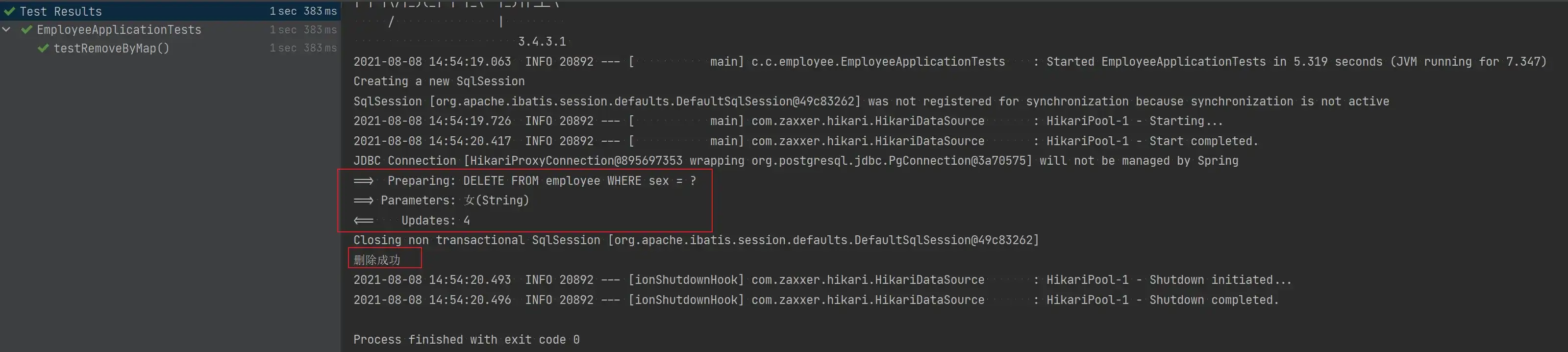
void testRemoveByMap() {
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("sex", "女");
Assert.assertTrue(employeeService.removeByMap(map));
System.out.println("删除成功");
}
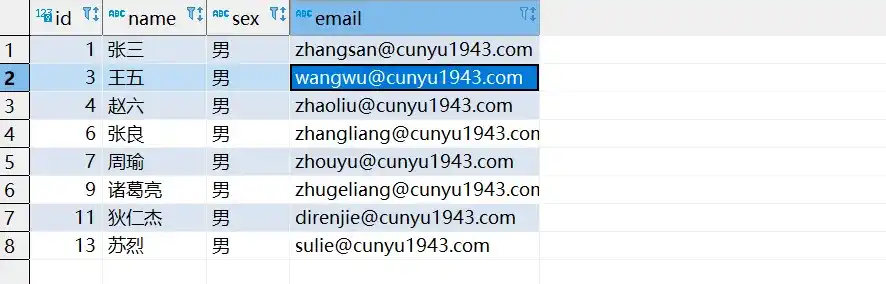
}- 测试结果
- 按条件删除后的数据库
- 根据 ID 批量删除
- 方法声明
// 删除(根据ID 批量删除)
boolean removeByIds(Collection<? extends Serializable> idList);- 批量删除实例
package com.cunyu.employee;
import com.cunyu.employee.entity.Employee;
import com.cunyu.employee.mapper.EmployeeMapper;
import com.cunyu.employee.service.EmployeeService;
import org.junit.Assert;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
@SpringBootTest
class EmployeeApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private EmployeeService employeeService;
@Test
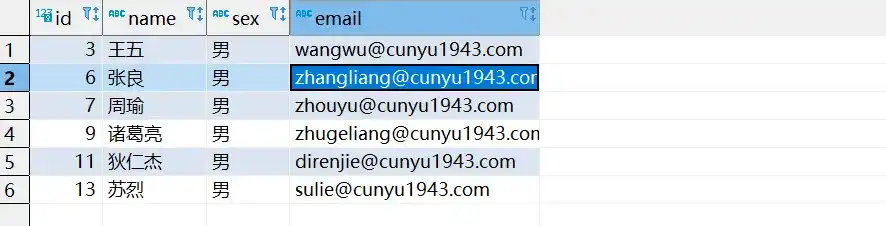
void testRemoveByIds() {
List<Integer> ids = new ArrayList<>();
ids.add(1);
ids.add(4);
Assert.assertTrue(employeeService.removeByIds(ids));
System.out.println("批量删除成功");
}
}- 测试结果
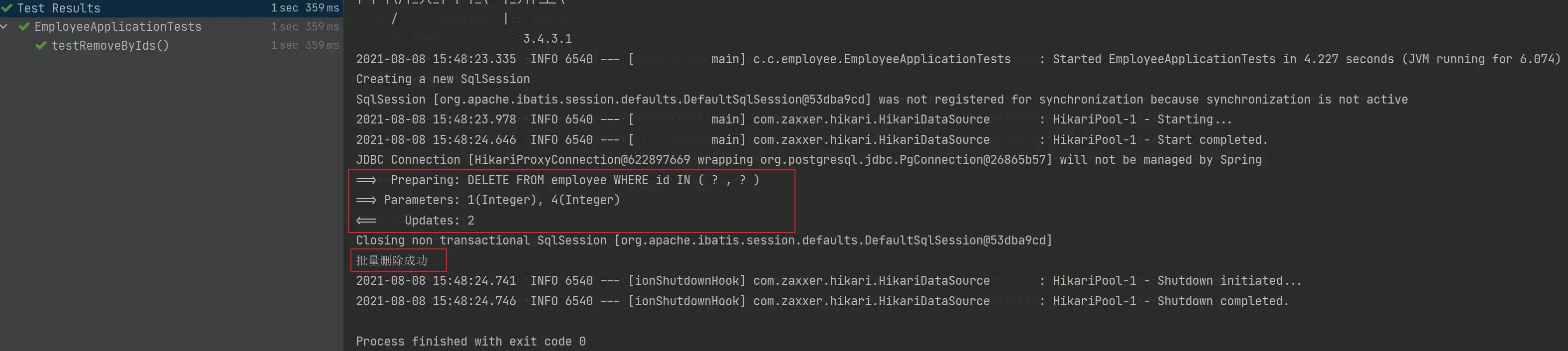
- 批量删除后的数据库
Update
- 根据 ID 选择修改
- 方法声明
// 根据 ID 选择修改
boolean updateById(T entity);- 根据 ID 修改实例
package com.cunyu.employee;
import com.cunyu.employee.entity.Employee;
import com.cunyu.employee.mapper.EmployeeMapper;
import com.cunyu.employee.service.EmployeeService;
import org.junit.Assert;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
class EmployeeApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private EmployeeService employeeService;
@Test
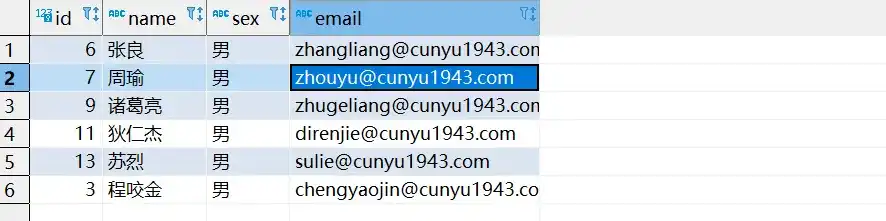
void testUpdateById() {
Employee employee = new Employee();
employee.setId(3L);
employee.setName("程咬金");
employee.setSex("男");
employee.setEmail("chengyaojin@cunyu1943.com");
Assert.assertTrue(employeeService.updateById(employee));
System.out.println("更新成功");
}
}- 测试结果
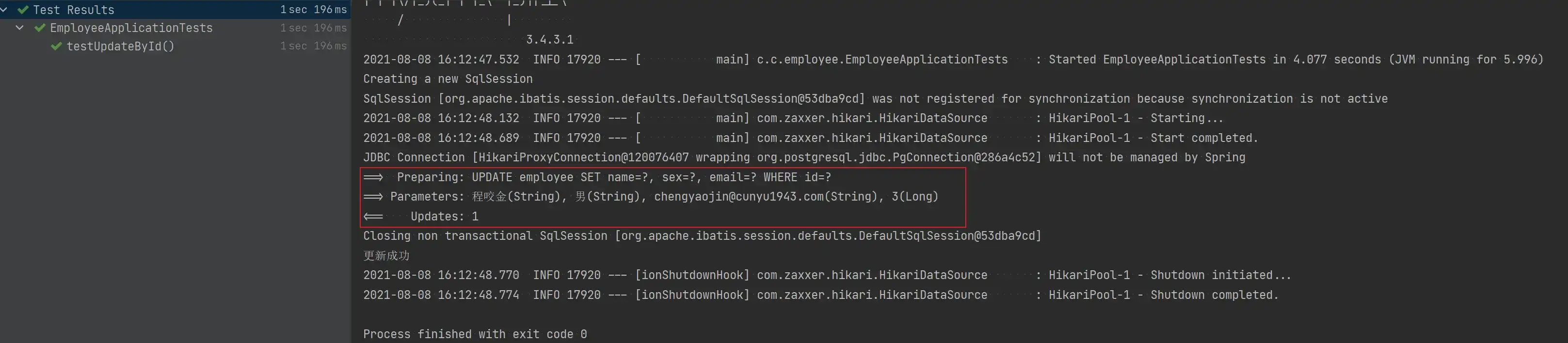
- 更新后的数据库
- 根据 ID 批量更新
2.1 统一更新
- 方法声明
// 根据ID 批量更新
boolean updateBatchById(Collection<T> entityList);- 批量更新实例
package com.cunyu.employee;
import com.cunyu.employee.entity.Employee;
import com.cunyu.employee.mapper.EmployeeMapper;
import com.cunyu.employee.service.EmployeeService;
import org.junit.Assert;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
@SpringBootTest
class EmployeeApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private EmployeeService employeeService;
@Test
void testUpdateBatchById() {
Employee employee1 = new Employee();
employee1.setId(6L);
employee1.setName("妲己");
employee1.setSex("女");
employee1.setEmail("daji@cunyu1943.com");
Employee employee2 = new Employee();
employee2.setId(13L);
employee2.setName("小乔");
employee2.setSex("女");
employee2.setEmail("xiaoqiao@cunyu1943.com");
List<Employee> employeeList = new ArrayList<>();
employeeList.add(employee1);
employeeList.add(employee2);
Assert.assertTrue(employeeService.updateBatchById(employeeList));
System.out.println("更新成功");
}
}- 测试结果
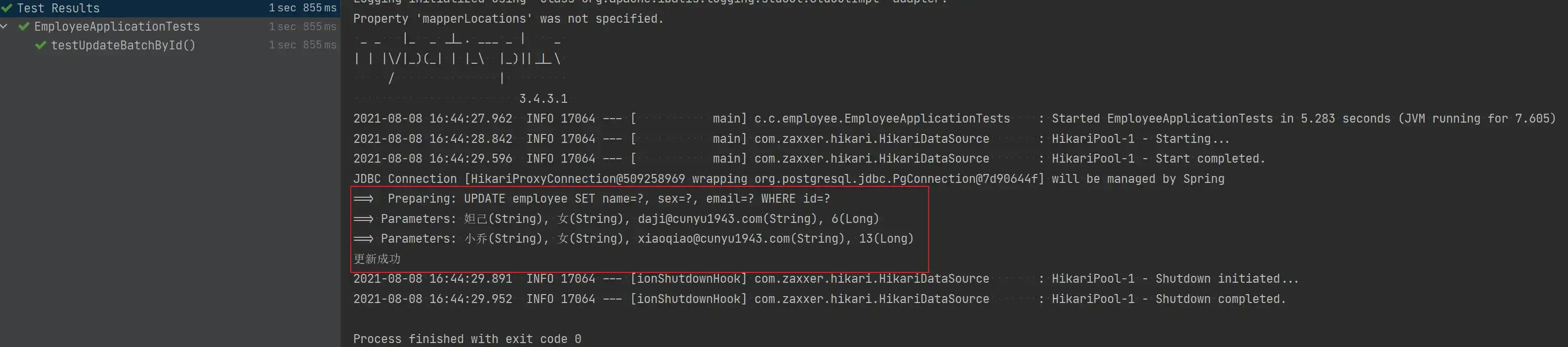
- 批量更新后的数据库
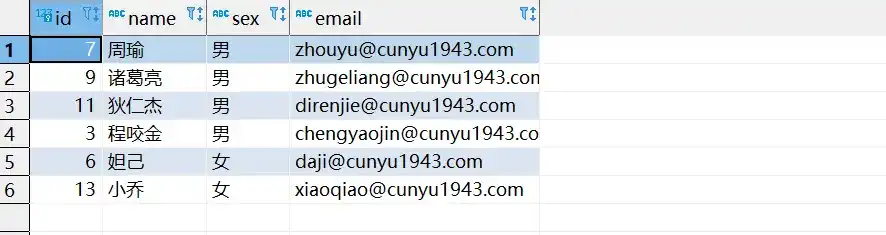
2.2 分批次更新
- 方法声明
// 根据ID 批量更新
boolean updateBatchById(Collection<T> entityList, int batchSize);- 分批次更新实例
package com.cunyu.employee;
import com.cunyu.employee.entity.Employee;
import com.cunyu.employee.mapper.EmployeeMapper;
import com.cunyu.employee.service.EmployeeService;
import org.junit.Assert;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
@SpringBootTest
class EmployeeApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private EmployeeService employeeService;
@Test
void testUpdateBatchById() {
Employee employee1 = new Employee();
employee1.setId(7L);
employee1.setName("武则天");
employee1.setSex("女");
employee1.setEmail("wuzetian@cunyu1943.com");
Employee employee2 = new Employee();
employee2.setId(3L);
employee2.setName("李元芳");
employee2.setSex("男");
employee2.setEmail("liyuanfang@cunyu1943.com");
List<Employee> employeeList = new ArrayList<>();
employeeList.add(employee1);
employeeList.add(employee2);
Assert.assertTrue(employeeService.updateBatchById(employeeList, 2));
System.out.println("更新成功");
}
}- 测试结果
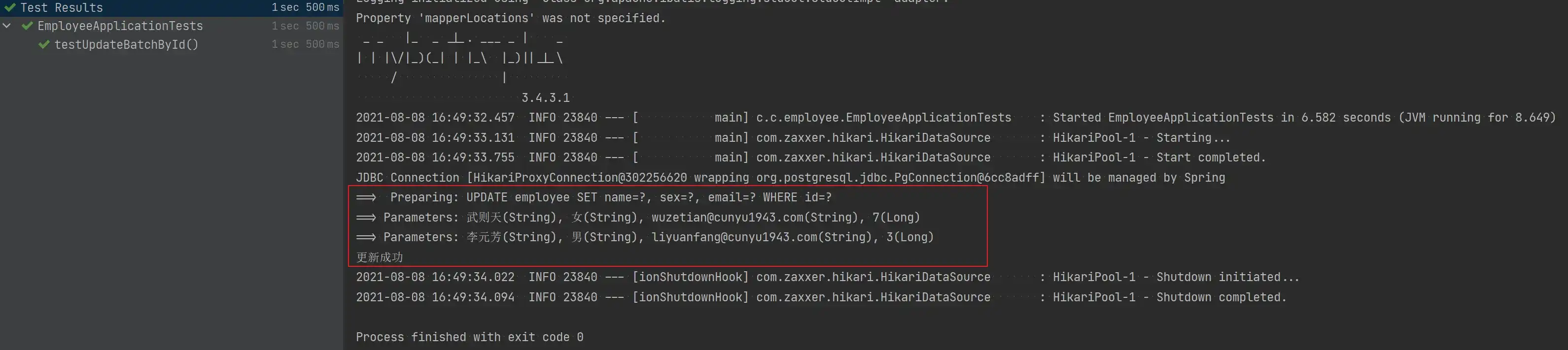
- 分批次更新后的数据库
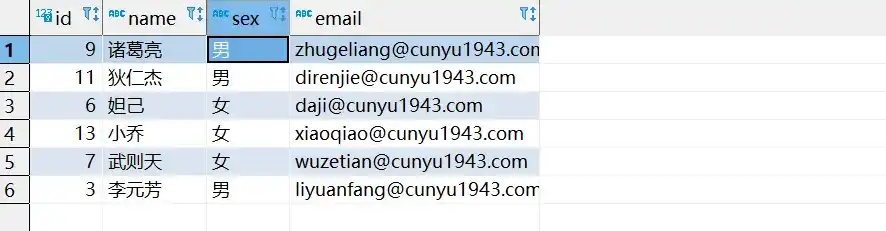
Get
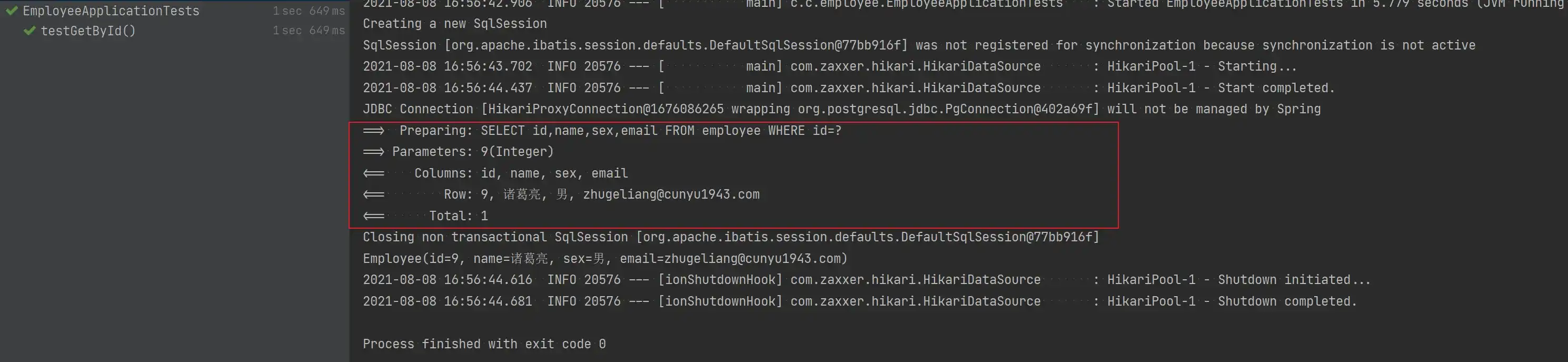
- 根据 ID 查询
将所要查询记录的 id 作为参数,然后将查询到的实体返回。
- 方法声明
// 根据 ID 查询
T getById(Serializable id);- 查询实例
package com.cunyu.employee;
import com.cunyu.employee.entity.Employee;
import com.cunyu.employee.mapper.EmployeeMapper;
import com.cunyu.employee.service.EmployeeService;
import org.junit.Assert;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
class EmployeeApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private EmployeeService employeeService;
@Test
void testGetById() {
Employee employee = employeeService.getById(9);
System.out.println(employee);
}
}- 测试结果
List
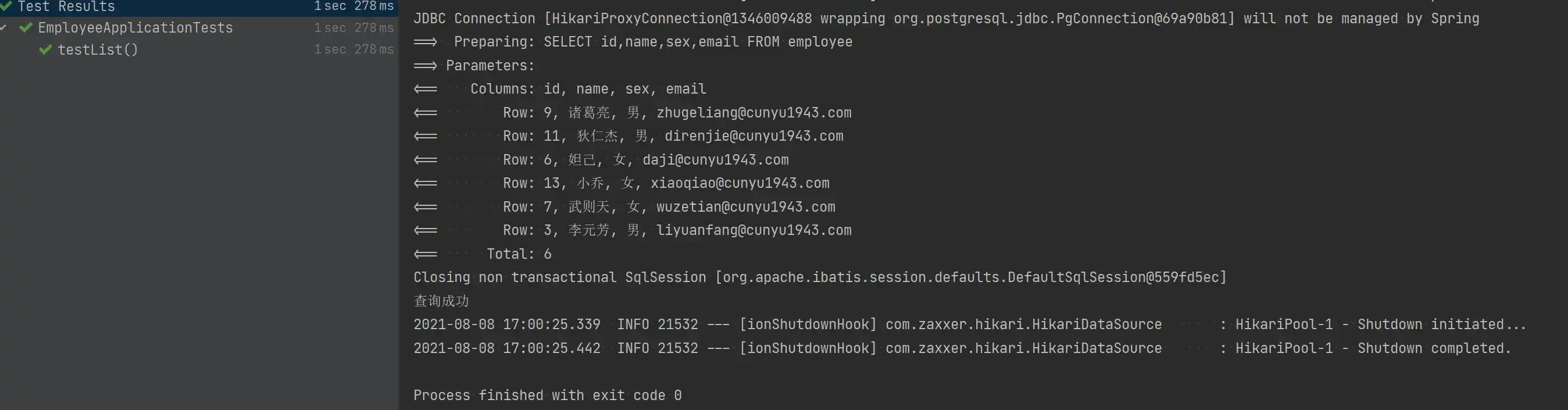
- 查询所有
查询所有记录,然后返回到一个集合中。
- 方法声明
// 查询所有
List<T> list();- 查询实例
package com.cunyu.employee;
import com.cunyu.employee.entity.Employee;
import com.cunyu.employee.mapper.EmployeeMapper;
import com.cunyu.employee.service.EmployeeService;
import org.junit.Assert;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
@SpringBootTest
class EmployeeApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private EmployeeService employeeService;
@Test
void testList() {
List<Employee> employeeLists = new ArrayList<>();
employeeLists = employeeService.list();
Assert.assertEquals(6, employeeLists.size());
System.out.println("查询成功");
}
}- 测试结果
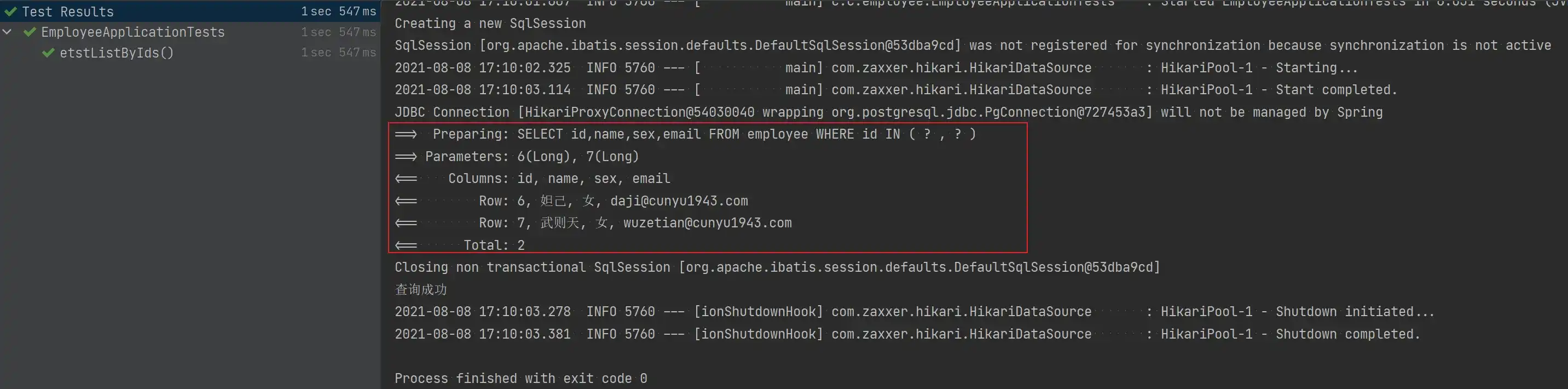
- 根据 ID 批量查询
讲所要查询的记录 id 传入集合,然后座位方法参数,最后返回查询到的结果到一个集合中。
- 方法声明
// 查询(根据ID 批量查询)
Collection<T> listByIds(Collection<? extends Serializable> idList);- 批量查询实例
package com.cunyu.employee;
import com.cunyu.employee.entity.Employee;
import com.cunyu.employee.mapper.EmployeeMapper;
import com.cunyu.employee.service.EmployeeService;
import org.junit.Assert;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
@SpringBootTest
class EmployeeApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private EmployeeService employeeService;
@Test
void testListByIds() {
List<Long> ids = new ArrayList<>();
ids.add(6L);
ids.add(7L);
Assert.assertEquals(2, employeeService.listByIds(ids).size());
System.out.println("查询成功");
}
}- 测试结果
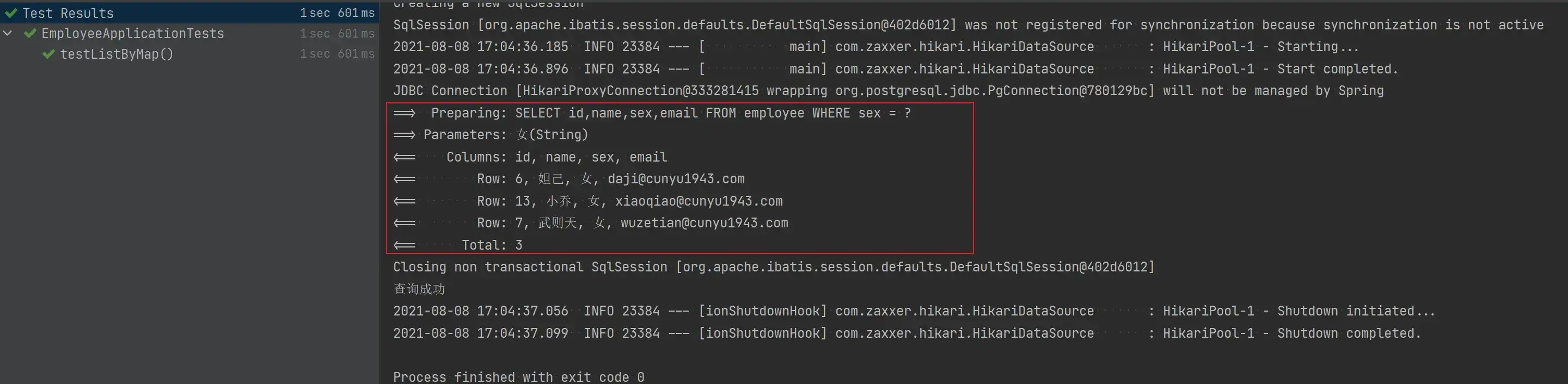
- 根据条件查询
条件传入 Map 集合,key 对应字段,value 对应值,然后返回集合。
- 方法声明
// 查询(根据 columnMap 条件)
Collection<T> listByMap(Map<String, Object> columnMap);- 根据条件查询实例
package com.cunyu.employee;
import com.cunyu.employee.entity.Employee;
import com.cunyu.employee.mapper.EmployeeMapper;
import com.cunyu.employee.service.EmployeeService;
import org.junit.Assert;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@SpringBootTest
class EmployeeApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private EmployeeService employeeService;
@Test
void testListByMap() {
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("sex", "女");
Assert.assertEquals(3, employeeService.listByMap(map).size());
System.out.println("查询成功");
}
}- 测试结果
- 查询所有列表
- 方法声明
// 查询所有列表
List<Map<String, Object>> listMaps();- 查询实例
package com.cunyu.employee;
import com.cunyu.employee.entity.Employee;
import com.cunyu.employee.mapper.EmployeeMapper;
import com.cunyu.employee.service.EmployeeService;
import org.junit.Assert;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
class EmployeeApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private EmployeeService employeeService;
@Test
void testListMaps() {
Assert.assertEquals(6, employeeService.listMaps());
System.out.println("查询成功");
}
}- 测试结果
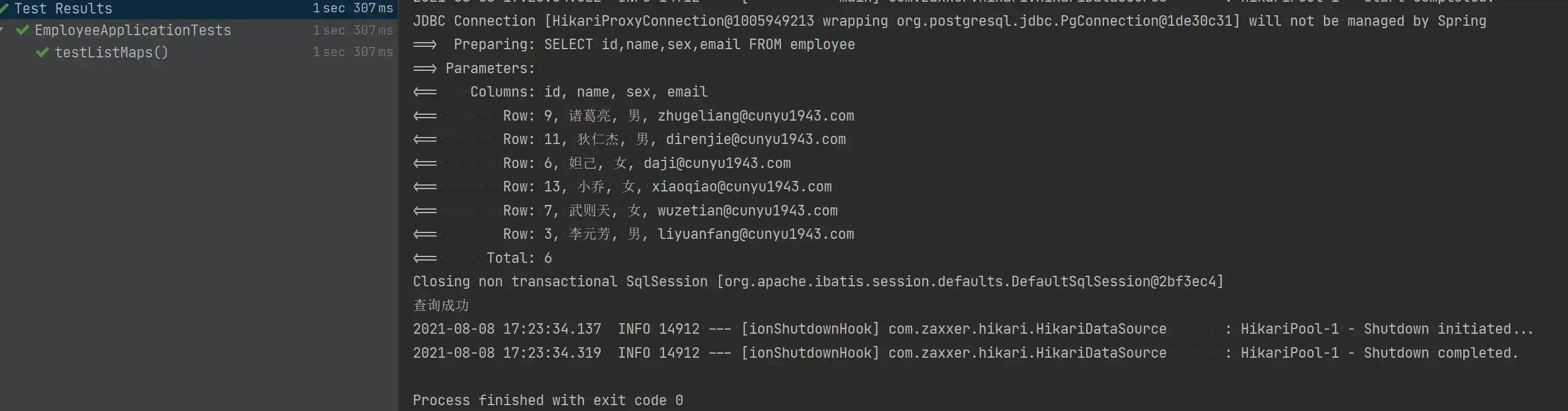
- 查询所有记录
用于查询所有数据记录,并将其返回到一个集合中。
- 方法声明
// 查询全部记录
List<Object> listObjs();- 查询实例
package com.cunyu.employee;
import com.cunyu.employee.entity.Employee;
import com.cunyu.employee.mapper.EmployeeMapper;
import com.cunyu.employee.service.EmployeeService;
import org.junit.Assert;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
class EmployeeApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private EmployeeService employeeService;
@Test
void testListObjs() {
Assert.assertEquals(6, employeeService.listObjs().size());
System.out.println("查询成功");
}
}- 测试结果
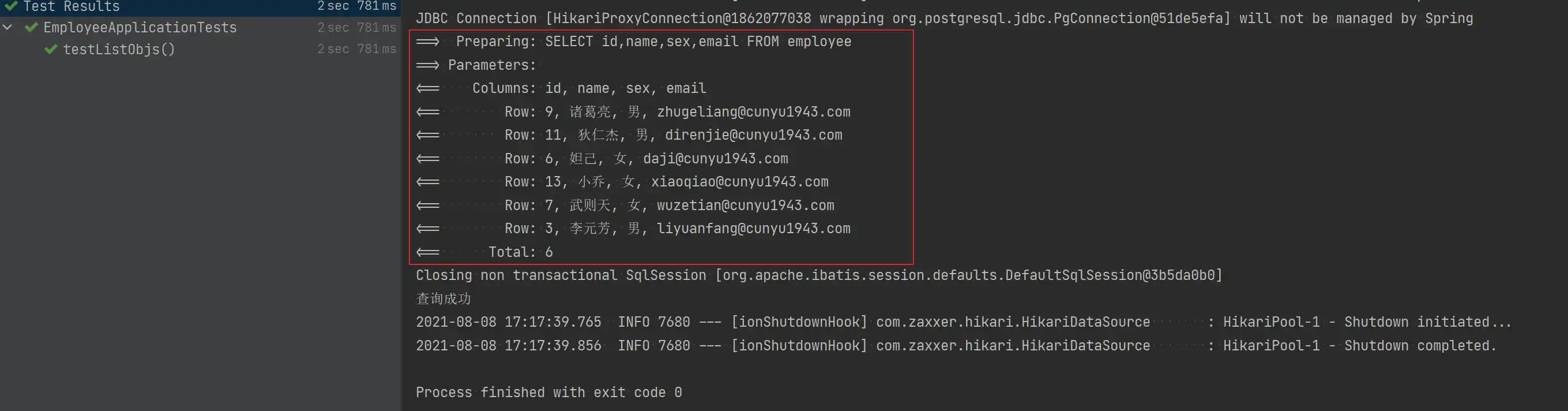
Count
- 查询记录总数
用于统计数据控中的记录总条数,方法返回记录条数。
- 方法声明
// 查询总记录数
int count();- 查询记录总数实例
package com.cunyu.employee;
import com.cunyu.employee.entity.Employee;
import com.cunyu.employee.mapper.EmployeeMapper;
import com.cunyu.employee.service.EmployeeService;
import org.junit.Assert;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
class EmployeeApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private EmployeeService employeeService;
@Test
void testCount() {
Assert.assertEquals(6, employeeService.count());
System.out.println("查询成功");
}
}- 测试结果
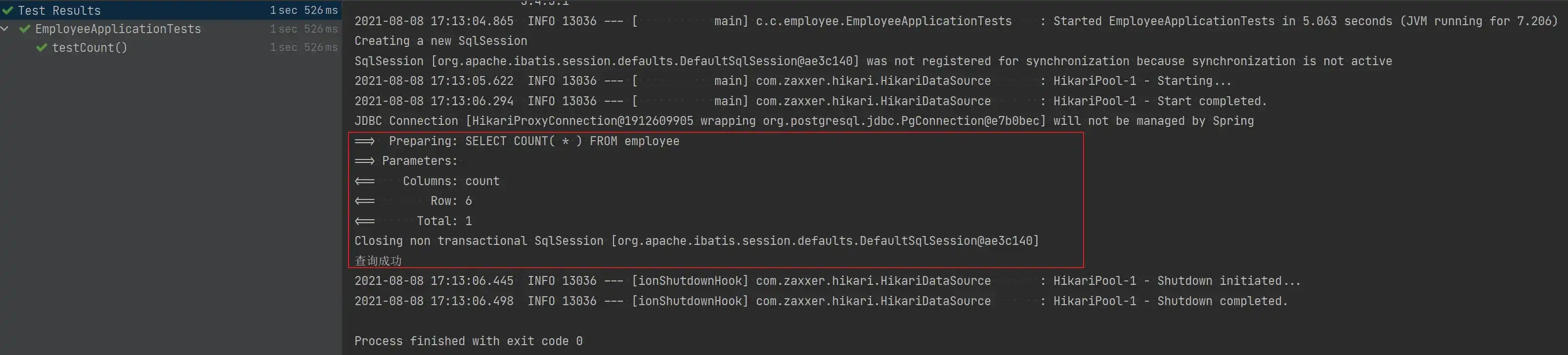
总结
好了,以上就是关于 Mybatis-Plus 的日志配置以及如何进行 CRUD 的相关内容了,这里 CRUD 主要又分为 Mapper 层和 Service 层,我们可以根据自己的需要进行选择。当然,在我们日常使用中,常常都是两个接口一起使用,关于更多 MP 的使用技巧,我们下期文章再见!



